A benchmark study of k-mer counting methods for high-throughput sequencing – a review paper
Catagories of k-mer counting methods
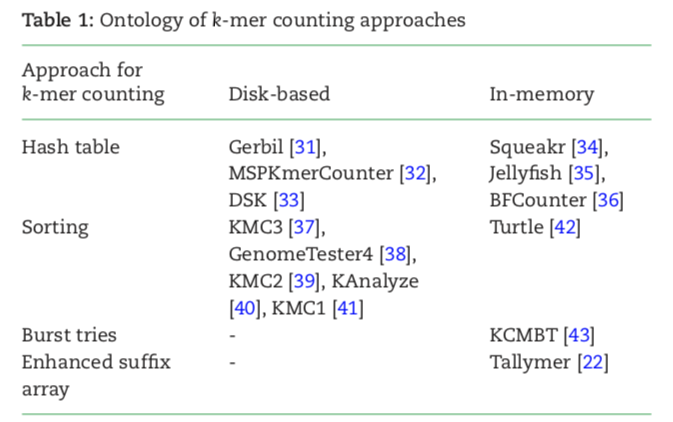
- Using the sorting approach
sorting all k-mers extracted from each read; Thus k-mer frequencies can be easily counted because, after sorting, repeating k-mers lay at adjacent positions in the sorted list.
sorting and compaction (SAC) -based algorithm ??
aTurtle[used] / cTurtle
Pattern Block Bloom Filter is a cache-friendly variant of the BLoom Filter, which has a very small cache miss ratio. - Using a hash table
k-mer are stored as keys and their counts are stored as values.
e.g. Jellyfish, lock-free hash table and Compare-and-swap(CAS) assembly instruction Jellyfish2, use an additional Bloom filter-based mode to remove all singleton k-mers. KAT - Using a Bloom Filter and its Variants and counting quotient filter
majority of any genomic dataset is made up of single-frequency k-mers, which mainly attributed to sequencing errors. A bloom filter is a probabilistic data structure used for dynamic membership query lookup. BFCounter. Squeaker: uses a counting filter data structure(counting quotient filter[CQF])
- Using the concept of super k-mer: minimizers and signatures
MSPKmerCounter is the 1st tool to implement MSP(Minimum Substring Partitioning) for k-mer counting.
KMC3.
Computation based on k-mer counts
- 计算基因组🧬的大小
把每个k-mer看作基因组中的一个碱基,通过k-mer分布 -> k-mer总数(T)和每个碱基平均出现的次数(u).
基因组大小 = T/u - 重复序列
?? 理论认为, 但拷贝序列k-mer,出现在主峰1.6倍以后的概率非常低;认为该区间为重复k-mer.
重复序列长度 = 重复k-mer序列总数/ u - 杂合率估算
Related Q&A
1.为啥组装时,k要选择基数?
只有奇数,才能保证每个kmer序列的反向互补Kmer与自身是不同的,从而避免了正反链混淆。
如 :5-mer的 CGCGC,反向互补后是 GCGCG, 它们是不同的;这就不会像 4-mer,CGCG发现它反向互补后仍然是CGCG