Title: CARE: Content-Aware Sequencing Read Error Correction
- a alignment-based method
- using minhash : for efficient similarity search
- GPU acceleration (handle human genome in only 4 hours)
- evaluation: false positive; true positive; superior de nove assembly
- written in C++ code
how to compare assembly results?
Content

1.Two catagories of the existing EC(error correction) methods:
- k-mer spectrum based methods
- multiple sequence alignment based methods
k-mer: inspect kmer spectrum; determine solid or weak kmer (trusted or untrusted) by choosing threshold (assuming that an errorneous kmer does not appear frequently); replace weak kmers by similar solid kmers;
weakness: may fail is in low coverage genomic regions where error-free k-mers are identified as weak since their frequency falls below the utilized abundance threshold.
e.g. SGA-EC (Simpson and Durbin, 2012), Musket (Liu et al., 2013), RACER (Ilie and Molnar, 2013), Lighter (Song et al., 2014), Blue (Greenfield et al., 2014), BFC (Li, 2015), BLESS (Heo et al., 2016), RECKONER (Długosz and Deorowicz, 2017), and Athena (Abdallah et al., 2019).
multiple sequence alignment (MSA) : build MSA; correct according to consensus MSA column; advantages: well performance on low coverage region compared with kmer-based methods weakness: higher computational complexity
e.g. Coral (Salmela and Schröder, 2011) and ECHO (Kao et al., 2011),Fiona (Schulz et al., 2014), Karect (Allam et al., 2015), Bcool (Limasset et al., 2019), and BrownieCorrector (Heydari et al., 2019) distinguished by utilized data structures (such as suffix trees/arrays, hash tables, or de Bruijn graphs)
2.challenges of MSA methods
- efficiently calculate similarity of reads to build MSA
- accurate and quick select candidate reads of a seed/anchor read
CARE uses minhash to approch the above aims
Jaccard Index
| S(A,B) = | A_∩_B | / | A∪B |
A,B 两个集合:A = {s1, s3, s6, s8, s9} ; B = {s3, s4, s7, s8, s10}
根据Jaccard Index公式,A,B的相似度 S(A,B) = |A_∩_B|/|A∪B| = 2/8 = 0.25
随机从两个集合中各挑选一个元素s(A)、s(B),刚好这两个无素相同的概率 其实等于 在A∪B这个大的随机域里,选中的元素落在A_∩B_这个区域的概率,这个概率就等于Jaccard的相似度!这就是MinHash的基本原理
找一个随机的哈希函数h,对集合的每一个元素作哈希运算,比如集合A,可以算出5个hash值,因为是随机的,这5个hash值里值最小的那个元素,对于A集合中所有元素概率都是均等的。同样方法从B中取最小hash值,2个minhash相等的概率就是集合的相似度了。
Minhash
Minhash a specific locality sensitive hashing subsampling technique (originally introduced 2000)
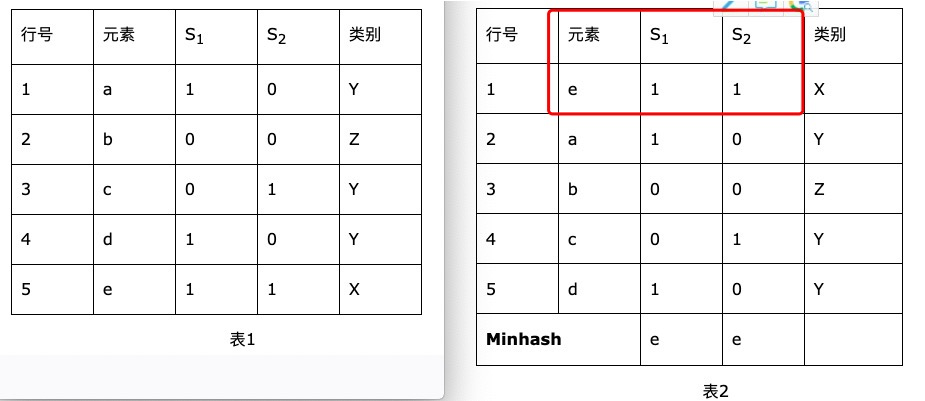
Minhash算法大体思路是:举个例子,S1 = {a,d,e},S2 = {c, e},设全集U = {a,b,c,d,e}。见表1;采用一种hash函数,将元素的位置均匀打乱,然后将新顺序下每个集合第一个元素作为该集合的特征值。比如哈希函数h1(i) = (i + 1) % 5,其中i为行号。作用于集合S1和S2
1.从特征矩阵 通过hash映射得到 signature矩阵
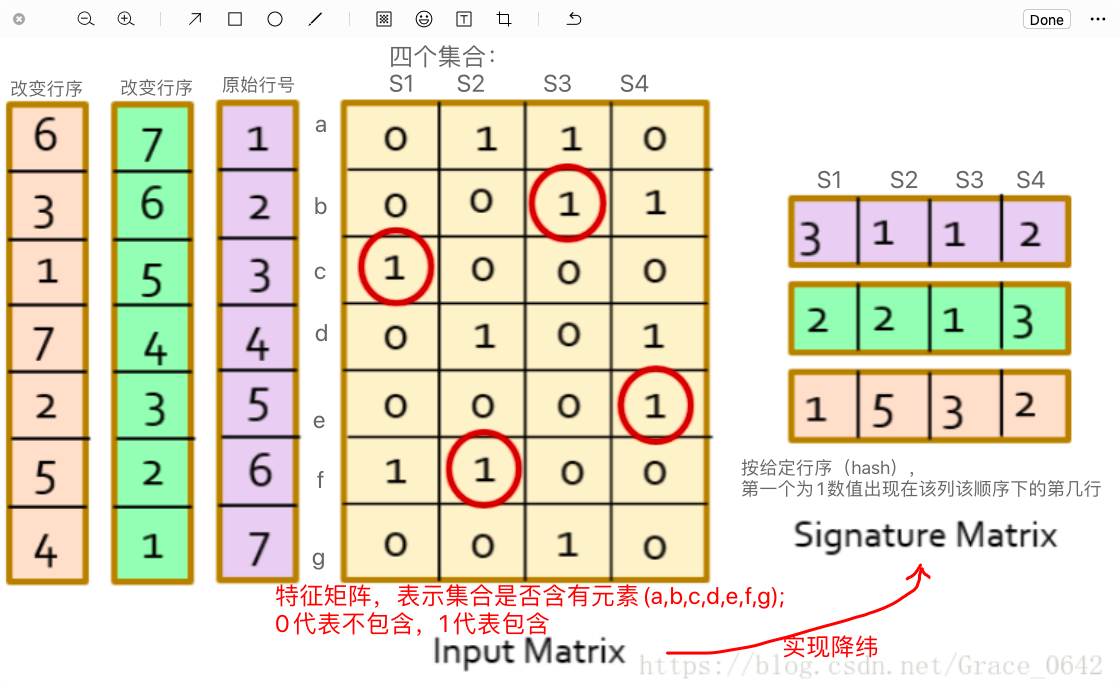
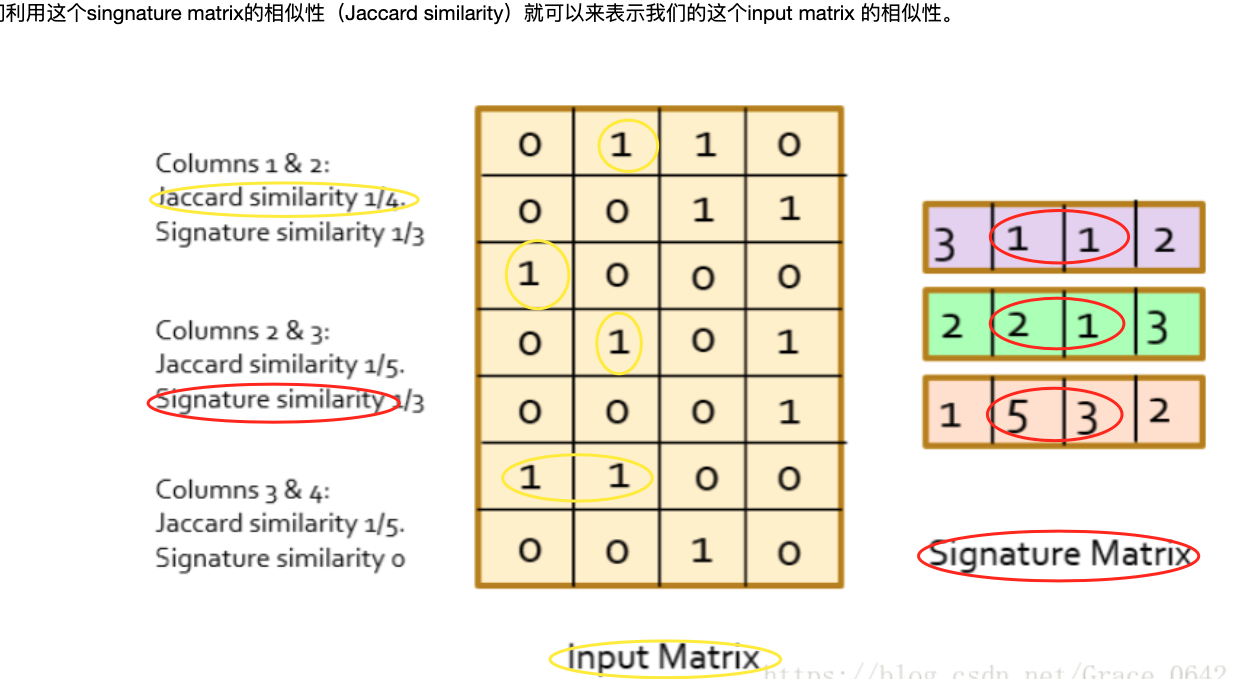
给出N个集合,找到相似的集合对,如何实现呢?直观的方法是比较任意两个集合。那么可以十分精确的找到每一对相似的集合,但是时间复杂度是O(n2)。Minhash和LSH(Locality-sensitive Hashing)来实现上述目的,在相似的集合较少的情况下,可以在O(n)时间找到大部分相似的集合对。
只需要找到N个哈希函数,对集合生成一组minhash,算两个集合的相似度,也就是这2组minhash中,交集/并集了。这个计算相对容易了,因为每个集合的元素数变成了常数N,也就是说,MinHash其实是一种降维技术。
LSH (Locality-Sensitive Hashing)
局部敏感哈希(Locality-Sensitive Hashing, LSH) 是一种解决在海量的高维数据集中查找与查询数据点(query data point)近似最相邻的某个或某些数据点的方法。 一种方法能够不遍历所有可能的元素对就找出相似度较大的那些(大于某个给定的阈值t),这就是所谓Locality-Sensitive Hashing
理论:两个相邻数据点通过相同的映射或投影变换(projection)后,这两个数据点在新的数据空间中仍然相邻的概率很大,而不相邻的数据点被映射到同一个桶的概率很小。
如果我们对原始数据进行一些hash映射后,我们希望原先相邻的两个数据能够被hash到相同的桶内,具有相同的桶号。 对原始数据集合中所有的数据都进行hash映射后,我们就得到了一个hash table,这些原始数据集被分散到了hash table的桶内,每个桶会落入一些原始数据,属于同一个桶内的数据就有很大可能是相邻的,当然也存在不相邻的数据被hash到了同一个桶内。
优缺点:LSH并不能保证一定能够查找到与query data point最相邻的数据,而是减少需要匹配的数据点个数的同时保证查找到最近邻的数据点的概率很大。
两种常见的LSH算法—— MinHash 和 SimHash
Innovation
- Using minhashing
CARE is based on a variant of minhashing to quickly find a set of candidate reads which are similar to a query read with high probability.